Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions Set 6 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- Question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C, D and E. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no.21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each, Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C contains Q.25 to Q. 29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no. from 34 to 36 are case based questions with three sub questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map based, carrying 5 marks with two parts. 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section A
Section A consists of 20 questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Why did most ‘conservative regimes’ impose censorship laws to control printed material associated with the French Revolution in 1815? Identify the appropriate reason from the following options. (1)
(a) Because conservative regimes were autocratic and wanted to preserve traditional institutions like church, monarchy and social hierarchies.
(b) Because freedom of press would lead to wide circulation of revolutionary ideas.
(c) Because conservative regimes were against the liberal notions.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 2.
Which place in India has an artificial lake to conserve water that dates to the 11th century? [1]
(a) Delhi
(b) Bhopal
(c) Mumbai
(d) Kolhapur
Answer:
(b) Bhopal
Question 3.
The following image depicts the fear of repression which drove many liberal nationalists underground. Which of the following events is marked as per the given image? Identify. (1)

(a) Signing of Treat of Vienna
(b) Founding of Young Europe in Berne, 1833
(c) Giuseppe Mazzini unifying Italy
(d) William I unifying Germany
Answer:
(b) Founding of Young Europe in Berne, 1833.
Question 4.
Which of the following options represent potential measures that can be taken to mitigate the threats posed by on the tiger population and biodiversity? [1]
(i) Banning hunting, giving legal protection to their habitats, and restricting trade in wildlife
(ii) Prohibiting the visit of public into forest area
(iii) Establishing wildlife sanctuaries and National Parks
(iii) Converting forests into Reserved and Protected forests
Options:
(a) Statements (i) and (ii) are correct.
(b) Statement (ii), (iii) & (iv) are correct.
(c) Statement (ii) is correct.
(d) Statements (i), (iii), & (iv) are correct.
Answer:
(d) Statements (i), (iii), & (iv) are correct.
Question 5.
Arrange the following nationalist events in a chronological order. (1)
I. Uttar Pradesh peasants organised by Ram Chandra.
II. Gandhiji organised Satyagraha in Kheda district of Gujarat.
III. Non-Cooperation and Khilafat Movement launched.
IV Gandhiji travelled to Champaran to inspire peasants against the oppressive plantation system.
Codes
(a) I, II, III, IV
(b) III, I, II. IV
(c) II, IV III, I
(d) IV, II, I, III
Answer:
(d) IV, II, I, III
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following statements accurately distinguishes between Majoritarianism and Power sharing? [1]
(a) Majoritarianism emphasizes the dominance of the majority community while Power sharing emphasizes the sharing of power among different groups.
(b) Majoritarianism emphasizes the need for consensus building, while Power sharing emphasizes the exclusion of minority groups.
(c) Majoritarianism emphasizes the importance of accommodating minority interests, while Power sharing emphasizes the need for majority rule.
(d) Majoritananism emphasizes the need for peaceful resolution of conflicts, while Power sharing emphasizes the use of force to impose the majority’s will.
Answer:
(a) Majoritarianism emphasizes the dominance of the majority community, while Power sharing emphasizes the sharing of power among different groups.
Question 7.
Identify the crop with the help of clues given below. (1)
It is a staple food crop for a majority of the people of India.
It is a Kharif crop that requires high temperature, high humidity with high annual rainfall of above 100 cm.
(a) Pulses
(b) Rice
(c) Wheat
(d) Maize
Answer:
(c) Wheat
Question 8.
Rahul has a sack of cotton but he needs wheat and Anush has a sack of wheat and needs cotton, under this situation both will be able to exchange their goods. In case of the absence of such coincidence of wants, they may not exchange their goods. Which one of the following would be the best option that describes the mutual exchange of goods and eliminates the exchange of goods? [1]
Options:
(a) Double coincidence of want, Exchanging commodity for commodity.
(b) Double Coincidence of want, Credit on Commodity.
(c) Double coincidence of wants, Loan on commodity.
(d) Double coincidence of wants, Money
Answer:
(d) Double coincidence of wants, Money
Question 9.
Vishakha wanted to start the rubber business. She consulted many stakeholders regarding the same. In such a meeting, she met Gaurav. Gaurav suggested to her to set up the rubber production unit. He told her that this Indian state produces around 74% of India’s total rubber production. And it would be economical for her if she established her rubber manufacturing plant in this state. According to your knowledge, which Indian state was recommended by Gaurav? (1)
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Assam
(c) Kerala
(d) Meghalaya
Answer:
(c) Kerala
Question 10.
Identify the painting from the options given below. [1]

(a) Frankfurt Parliament
(b) Reichstag
(c) Duma
(d) The House of Parliament
Answer:
(a) Frankfurt Parliament
![]()
Question 11.
Consider the following statements regarding the sources of revenue in a federal system. (1)
I. States are provided with unlimited financial powers.
II. States are dependent for revenue on the Central Government.
III. The Central Government has no financial autonomy.
IV. The sources of revenue for each level of government are specified in the Constitution of India to ensure its financial autonomy.
Select the correct option
(a) Only I
(b) Both I and II
(c) Both II and III
(d) Only IV
Answer:
(d) Only IV
Question 12.
Choose the correct option to complete the statement.
If a government provides its citizens a right and means to examine the process of decision, it is …………………… .[1]
(a) an accountable government
(b) a responsible government
(c) a transparent government
(d) a stable government.
Answer:
(a) an accountable government
Question 13.
There are two statements marked as Assertion
(A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below. (1)
Assertion (A) Suppose the literacy rate in a state is 78% and the net attendance ratio in the secondary stage is 47%.
Reason (R) More than half of the students are going to other states for elementary education.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false
Question 14.
If there is a disruption by transporters and lorries refuse to transport vegetables, milk, etc. From rural areas to urban areas, food will become scarce in urban areas, whereas farmers will be unable to sell their products. Which of the following sectors will be affected due to this situation stated above? [1]
(a) Primary and Secondary
(b) Secondary and Tertiary
(c) Tertiary, Primary and Secondary
(d) Tertiary and Primary
Answer:
(c) Tertiary, Primary and Secondary
Question 15.
Tamilians during the 1980s formed various political organizations. Identify the reason from the given options.
(a) Their demand for a separate state was denied.
(b) Their demand for separate elections to provinces populated by the Tamils was denied.
(c) Their demand for more autonomy to provinces populated by the Tamils was repeatedly denied.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Their demand for more autonomy to provinces populated by the Tamils was repeatedly denied.
Question 16.
“M” gave his friend clues about a type of soil that suits for growing cotton. Which of the following clues provided by “M” would be most useful in identifying the ideal type of soil? [1]
Clues:
(i) It is well-known for its capacity to hold moisture.
(ii) It turns yellow when it is hydrated.
(iii) It is rich in kankur and bhangar nodules.
(iv) It is a well-drained loamy soil.
(a) Clue (i)
(b) Clue (i) and (iii)
(c) Clue (i) and (ii)
(d) Clue (iv)
Answer:
(a) Clue (i)
Question 17.
Why the Tertiary sector is becoming an important sector in India? Identify the reason for the given options. (1)
(a) Because it provides basic services to the people.
(b) Because basic facilities like public transportation, and health come under the public sector.
(c) Because it works on profit maximization.
(d) Both (a) and (b).
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 18.
The process of integration between different countries is called as ……………………. . [1]
(a) Privatization
(b) Globalization
(c) Liberalization
(d) Competition
Answer:
(b) Globalization
![]()
Question 19.
How one can generate employment opportunities in urban areas?
(a) Increase vocational education.
(b) Improve local and inter-city transportation facilities.
(c) Increase reservations in jobs.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 20.
Miss “S” approached a bank nearby to avail a loan for her own business, as well as a Self-help group which is operating in her village, the bank rejected her loan application whereas the Self-help group agreed to support her by providing the loan. Which one of the following documents is required by the bank, but not required by the self-help group to approve Miss “S’s” loan application for her business? [1]
(a) Application for loans
(b) Arrangement Letter
(c) Document on Collateral
(d) Demand promissory note and take delivery letter.
Answer:
(c) Document on Collateral.
Section B
Section B consists of 4 questions of 2 marks each
Question 21.
Study the map thoroughly and mention any one major fruit that is cultivated in the highlighted Indian state. (2)
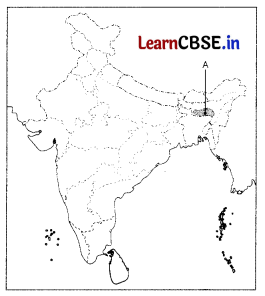
Answer:
Meghalaya is one of the major pineapple-producing states of India It contributes 8% of the total pineapple produced in India.
Question 22.
(A) “The most powerful weapon of the Spanish conqueror was not a conventional military weapon at all.” Justify the above statement by giving two reasons. [21
OR
(B) “Traders and travellers introduced new crops to lands they travelled. “Substantiate this statement with illustrations.
Answer:
(A)
- Spanish conquerors won America with not a conventional military weapon but with germs like smallpox which spread deep into the continent before any European could reach there.
- America’s original inhabitants had no immunity against these diseases that came from Europe. This disease erased the whole community, leading to conquest. This biological warfare in the mid-sixteenth century made it easy for Spanish to overpower the Americans.
OR
(B)
- It is believed that noodles travelled west from China to become Spaghetti. Or, perhaps Arab Traders took Pasta to fifth-century Sicily, an island now in Italy. Similar foods were also known in India and Japan, so the truth about their origins may never be known.
- Many of our common foods such as potatoes, soya, groundnuts, maize, tomatoes, chilies, sweet potatoes, and so on were not known to our ancestors until about five centuries ago. These foods were only introduced in Europe and Asia after Christopher Columbus accidentally discovered the vast continent that would later become known as the Americas.
Question 23.
In your own words. Write a brief newspaper note on the Simon Commission. (2)
Answer:
Simon Comrnssion arrived in India in 1928. t was greeted with black flags and slogans like Simon Go Back Both Congress and the Muslim League unitedly protested against it. This Commission was boycotted by the Indian people as it did not include any Indian members in it.
Question 24.
Mention any two reasons to state that India is a federal country.
Answer:
The following are the reasons to state that India is a federal country:
(i) Division of Powers: The Constitution of India demarcates the powers of the Central and State governments, and both have their separate areas of jurisdiction. The Seventh Schedule of the Indian Constitution lists the Union List, State List, and Concurrent List, which define the powers and responsibilities of the Central and State governments.
(ii) Independent Judiciary: India has an independent judiciary with the power of judicial review. The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial authority in the country and has the power to interpret the Constitution and resolve disputes between the Central and State governments.
(iii) Representation of States: The Rajya Sabha, the Upper House of the Indian Parliament, represents the States and Union Territories of India. The members of the Rajya Sabha are elected b the elected members of the Legislative Assemblies of the States and Union Territories.
Section C
Section C consists of 5 questions of 3 marks each
Question 25.
Analyze the graph properly and answer the following questions. (1+2)
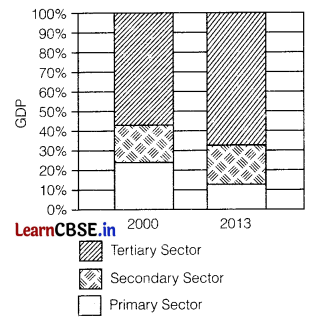
(a) What are the conclusions you can derive for primary and secondary activities?
(b) State the reason which supports the increasing role of the tertiary sector in Indian GDP.
Answer:
(a) The conclusion deriving from the primary and secondary activities are
The share of the primary sector and the secondary sector in Indian GDP has decreased in a significant manner
(b) The importance of the tertiary sector is rising because of the following reasons
- This sector provides basic services such as hospitals, educational institutions, post and telegraph services, police stations, and courts. municipal corporations. defense, banks, insurance, etc which are basic for the development of the country.
- This sector provides services Such as transport, trade, storage, etc which help in the development of agriculture or the primary sector, and the industries or the secondary sector.
![]()
Question 26.
(A) A worker in an urban area, who was working in a small factory was not paid his wages properly, he was forced to work extra hours under poor working conditions, there was no job security, recently he lost his job and was found selling electrical items in a pushcart. [3]
Analyze the role of the government in protecting the workers working in an Unorganized sector.
OR
(B) Mr. Pawan, a village head wanted to create more job opportunities to increase the income of the people of his village under the MGNREGA acts, Suggest any three activities, so that Mr. Pawan could initiate in his village.
Answer:
(A) The following are how the workers in the unorganized sector can be protected by the government:
- The small factories must be registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations which are given in various laws such as the Factories Act, Minimum Wages Act, Payment of Gratuity Act, Shops and Establishments Act, etc.
- The government can provide loans to help unemployed educated youth to start their own business.
- The workers are supposed to get medical benefits and, under the laws, the factory manager has to ensure facilities like drinking water and a safe working environment.
OR
(B) Under the MGNREGA Act, he can initiate the following activities to increase the income of the people living in his village:
- Cleaning the pond: Cleaning and maintaining water bodies such as lakes and ponds can help to improve the quality of water and make it suitable for irrigation purposes. This can lead to increased agricultural productivity, which, in turn, can increase the income of the farmers. Additionally, cleaning of the pond can provide employment opportunities for the local people.
- Construction of village roads: The construction of village roads can improve connectivity and accessibility within the village, making it easier for people to commute to work or transport goods. This can help to increase economic activity in the village, creating more job opportunities and boosting the income of the local people.
- Cooperative milk society/small-scale industry: The formation of a cooperative milk society can provide a platform for the local dairy farmers to collectively sell their milk and other dairy products, increasing their income. Similarly, the establishment of a small-scale industry can generate employment opportunities and create a market for local products, which can further contribute to increasing the income of the people.
- Construction work: The construction of houses, community centers, and other infrastructure projects can generate employment opportunities for the local people, helping to boost their income. This can also improve the living standards of the villagers, making it a sustainable solution for poverty reduction.
Question 27.
“Democracies have had a greater success in setting regular free and fair elections.” Analyse the statement.
Answer:
Democracies have had a greater success in setting regular free and fair elections in the following ways
- Every democracy holds elections and it has different political parties and guarantees the voting rights of its citizens.
- Every citizen in democracy has the right to elect his ‘leader and has control over the rulers.
- In democracy. whenever possible and necessary, citizens participate in decision-making that affects them.
- Democracy practice regular free and fair elections, This differentiates democracy from another form of government.
Question 28.
The Indian constitution provides three lists to distribute the legislative power. State any two subjects that are included in the union list. In which list the subject 11 Education” is included and why? [3]
Answer:
(i) The Indian Constitution has a three-fold distribution of legislative power, which contains three lists: The Union List, the State List, and the Concurrent List. The subjects that are included in the Union List are those that are under the exclusive jurisdiction of the Union Government.
(ii) Some of the subjects that are included in the Union List are defense of the country, foreign affairs and relations, banking, currency, and coinage, railways and air transport, posts and telegraphs, census and statistics, copyrights, patents and trademarks.
(iii) The subject “Education” comes under the Concurrent List, which means that both the Union Government and the State Governments have the power to make laws on this subject. The Concurrent List contains subjects that are of common interest to both the Union and the State Governments.
Question 29.
Hemant lives in an urban area where there is a shortage of water resources. So, he decided to do rooftop rainwater harvesting.
Do you agree that rooftop rainwater harvesting is quite beneficial for urban people? If yes, then why? (3)
Or
“Water scarcity may’ be an outcome of a large and growing population in India. Analyze the statement.
Answer:
Yes, I agree that rooftop rainwater harvesting is quite beneficial for urban people. The rainwater harvesting system is one of the best methods, practiced and followed to support the conservation of water.
The benefits of the rainwater harvesting system are listed below
- Helps in reducing the water bill,
- Decreases the water demand.
- Reduces the need for imported water.
- Promotes both water and energy conservation,
- Improves the quality and quantity of groundwater.
- Does not required a filtraton system for landscape irrigation.
- Does not require a filtration system for landscape irrigation
- This technology is relatively simple, easy to install and operate.
- It reduces soil eroson, stormwater runoff, flooding, and pollution of surface water with fertilises, pesticides, metals and other sediments
Or
Water scarcity may be an outcome of large and growing population in India. It can be analysed through the following points
- Post-independent India witnessed intensive industrialization and urbanisation. This situation increased water demand.
- The growing demand of water by the growing population leads the over-exploitation of water resources for various purposes.
- For example, for drinking, domestic uses, agriculture, electricity generation, and so on.
- Increasing urban centers with large and dense populations and urban lifestyles have not only added to water and energy requirements but have further aggravated the prob’em of water scarcity.
![]()
Section D
Section D consists of 4 questions of 5 marks each
Question 30.
(A) Analyze the impact of mining activities on the local environment and the health of the surrounding communities. [5]
OR
(B) “Non-conventional resources are the best option to conserve natural resources” Substantiate this statement with examples.
Answer:
(A)
- The miners are prone to inhaling the dust and noxious fumes that make them vulnerable to pulmonary diseases. There is also a risk of mine roofs collapsing.
- The miners are at a constant risk of inundation and fires in coal mines.
- Mining hurts the environment as it produces a lot of waste.
- Mining disrupts the local flora and fauna and contaminates the local water sources.
- It can also require the removal of the topsoil, leading to soil erosion.
OR
(B)
- Non-conventional resources are also known as renewable sources of energy. Examples of non-conventional sources of energy include solar energy. bioenergy, tidal energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, natural gas, etc.
- They are inexhaustible and renewable. They are also considered as clean sources of energy.
- Optimal use of resources of energy minimizes environmental impact and non-conventional resources produce minimum secondary waste compared to conventional sources.
- The growing consumption of energy has resulted in the country becoming increasingly dependent on fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas. Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties about the security of energy supply in the future, which in turn, has serious repercussions on the growth of the national economy.
- Natural gas is considered an environment-friendly fuel because of low carbon emissions. It does not cause air pollution or environmental degradation. Thus, it is the fuel for the present century.
- Renewable energy resources provide an excellent opportunity for mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions and reducing global warming through substituting conventional energy sources.
Question 31.
Explain the limited participation of Dalits in the Civil Disobedience Movement. (5)
Or
Discuss the Salt March and make clear why it was an effective symbol of resistance against colonialism. (5)
Answer:
Dalit participation was limited in the Civil Disobedience Movement, This can be explained in the following ways
Dalit or untouchables belong to the lower strata of our society. The Congress Party ignored the Dalits for fear of offending the conservative high-caste Hindus i.e. sanatanis. Gandhiji first realised that Swaraj would not come for a hundred years if untouchability was not eliminated, But, many Dalit leaders believed in a different political solution to the problem of their
community.
Dalits thought that only political empowerment would resolve their problem of social disabilities.
Dr. Ambedkar demanded a separate electorate for Dalits. which was denied by Gandhiji Oahts began organising themselves, demanding reserve seats in educational institutions and a separate electorate that would choose the Dalit members for legislative councils.
Dalit Movement continued to be apprehensive of the Congress-led national movement. Due to these above reasons. Datit’s their participation was limited in the Civil Disobedience Movement.
Or
Gandhi reached Dandi on 6th April, 1930 and violated Salt law by manufacturing salt from seawater, Breaking the Salt law was an apparent defiance of British authority and was a direct challenge to British rule in India.
people were not only asked to refuse cooperation with the British. but to break the unjustified colonial laws, Thousands of people from different parts of the country broke the Salt law, manufactured it, and demonstrated in front of government salt factories. With the spread of the movement. foreign cloth was boycotted, liquor shops were picketed, peasants refused to pay revenue, chaukidari taxes, village officials resigned, forest people violated forest laws by collecting wood and grading their cattle in the forest. Sali March inspired people from different segments of our society and became our effective tool of resistance against the colonial power.
Salt March was an effective symbol or tod of resistance against colonialism because All classes could identify with salt as it was an essential food item. Tax on salt and the monopoly over its manufacturing was a sign of the oppression of British rule.
![]()
Question 32.
(A) Analyse the role of a multiparty system in a democratic country like India. [5]
OR
(B) Evaluate the significant distinction between the national and regional parties and assess the requirements for a regional party to become a national party.
Answer:
(A)
- In a democracy like India, multiparty politics plays a crucial role in representing the diverse interests and aspirations of the citizens. It allows for a competitive and dynamic political environment where parties with different ideologies and agendas can participate and compete for the support of the electorate.
- A multiparty system provides a check and balance against any one party becoming too powerful and dominant.
- People can choose between several candidates as this system allows a variety of interests and opinions to enjoy political representation.
- Different and diverse parties could be representing the sections of society and power does not get absorbed in the hands of one single party.
- India adopted this system because of the vast diversity and plurality of the nation.
(B)
OR
| National Parties | Regional Parties |
| They are powerful in the entire nation and deals with national issues. | Their power is limited to a specific region or state, and only the demands of a specific region is discussed by them. |
| Their actions offer preference to national issues. | Their action offer preference to regional issues. |
| Their operations spans over the entire nation. | Their operations are confined to the state. |
| A party must gain at least six percent of the total votes in Lok Sabha or assembly elections in four states to become a national party. | A party must receive at least six percent of the total votes in the assembly election to become a regional party and win at least two seats. |
| Example – BJF, Congress, BSP, etc. | Example – DMK, Aam Admi Party, etc. |
Question 33.
Evaluate the term communa1 politics’. Also, explain the idea behind communal politics. (1+4)
Or
Is it correct to state that it is not politics that gets caste-ridden, but it is the caste that gets politicized? If yes, explain.
Answer:
The use of religion in politics, where one religion is shown as superior to other religions is called communal politics. Here, one religious group is against the other religious group and the demands of one religious group are against the demands of the other religious group.
The idea behind communal politics is
- Communal politics is based on the idea that religion is the only basis of forming a community.
- It believes that followers of one religion belong to the same community. Their interests, ideas, and opinions are the same.
- Communal politics follows that people belonging to different religions cannot be a part of the same community. Their ideas and demands are bound to be different.
- In an extreme case of communalism, communal politics follows that people from different religions are not equal citizens and cannot live together within one nation, which leads to partition of that country.
- Communal politics is a belief that a particular community has same voice is fundamentally wrong. People of one religion do not have the same interests and aspirations in every context. All voices inside a community have a right to be heard.
Or
Yes, it is correct to say that it is riot politics that gets caste-ridden, but it is the caste that gets politicised. - Caste can take various forms in politics as Each caste group tries to become bigger by incorporating within it neighboring castes or sub-castes which were earlier excluded from it.
- Various caste groups are required to enter a coalition with other castes or communities and thus enter a dialogue and negotiation.
- New kinds of caste groups have come up in the political arena like ‘backward’ and ‘forward’ caste groups.
- Caste plays different kinds of roles in politics In some cases, politics gives many disadvantaged communities, the opportunity to demand their share of power.
Section E
Section E consists of 3 Case-based questions of 4 marks each
Question 34.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
It is said that “passive resistance” is the weapon of the weak, but the power which is the subject of this article can be used only by the strong. This power is not passive resistance; indeed, it calls for intense activity. The movement in South Africa was not passive but active ‘Satyagraha is not physical force. Satyagraha does not inflict pain on the adversary; he does not seek his destruction … In the use of satyagraha, there is no ill will whatever. ‘Satyagraha is pure soul force.
Truth is the very substance of the soul. That is why this force is called satyagraha. The soul is informed with knowledge. In it burns the flame of love. … Nonviolence is the supreme dharma …‘ It is certain that India cannot rival Britain or Europe in force of arms. The British worship the war god and they can all of them become, as they are becoming, bearers of arms. The hundreds of millions in India can never carry arms. They have made the religion of non-violence their own.
In his famous book Hind Swaraj (1909) Mahatma Gandhi declared that British rule was established in India, with the cooperation of Indians, and had survived only because of this cooperation. If Indians refused to cooperate, British rule would collapse within a year.
Question 34.1.
Why did Gandhiji say that passive resistance is not the weapon of the weak? [1]
Answer:
Passive resistance calls for intensive activity which can only be used by the strong. This is why Gandhiji said that passive resistance is not the weapon of the weak.
Question 34.2.
“Satyagraha is pure soul force.” Substantiate this statement in 20 words. [1]
Answer:
Satyagraha uses the force of truth which itself is the substance of the soul that is informed with knowledge. This is why satyagraha is pure soul-force.
Question 34.3.
What according to Mahatma Gandhi is the best weapon to use to collapse British rule in India?
Answer:
In his book Hind Swaraj, Gandhiji declared that non-cooperation would be the best weapon to collapse British rule in India. It was only because of the Indian cooperation that the British were able to set their rule here.
Question 35.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
Decaying plants in swamps produce peat which has a low carbon and high moisture content and low beating capacity. Lignite is
low-grade brown coal, which is soft with high moisture content. The principal lignite reserves are in Neyveli in Tamil Nadu and are used for generation of electricity. Coal that has been buried deep and subjected to increased temperatures is bituminous. h is the most popular coal in commercial use. Metallurgical coal is high-grade bituminous coal which has a special value for smelting iron in blast furnaces. Anthracite is the highest quality hard coal.
In India, coal occurs in rock series of two main geological ages, namely Gondwana, a little over 200 million years in age and in
tertiary deposits which are only about 55 million years old. The major resources of Gondwana coal, which are metallurgical coal, are located in Damodar Valley (West Bengal, Jharkhand). Jharia, Raniganj, Bokaro are important coalfields. The Godavari, Mahanadi, Son, and Wardha valleys also contain coal deposits. Tertiary coals occur in the North-Eastern states of
Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
(i) Which reserves in Tamil Nadu is an important source of lignite in India? (1)
(ii) What is bituminous coal? Also, evaluate its any one property. (2)
(iii) State the reason due to why coal is associated with geological ages. (1)
Answer:
(i) Neyveh reserves in Tamil Nadu are important lignite reserves in India,
(ii) Bituminous coal is a high-grade coal and thus, is a metallurgical coal. This type of coal has a special value for smelting iron in blast furnaces. An important property of bituminous coal is that it is buried deep under the Earth’s surface and is subjected to increased temperature.
(iii) Coal is associated with geological ages because coal is formed due to compression of plant material and takes millions of years to come into existence.
Question 36.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human being need. Whatever people like, and should have, they will be able to get with greater income. So, greater income itself is considered to be one important goal. Now, what is the income of a country? Intuitively, the income of the country is the income of all the residents of the country. This gives us the total income of the country. However, for comparison between countries, total income is not such a useful measure. Since, countries have different populations, comparing total income will not tell us what an average person is likely to earn. Are people in one country better off than others in a different country? Hence, we compare the average income which is the total income of the country divided by its total population.
The average income is also called per capita income. In World Development Reports, brought out by the World Bank, this criterion is used in classifying countries. Countries with per capita income of US$ 49,300 per annum and above in 2019, are called high-income or rich income or rich countries and those with per capita income of 125$ 2,500 or less are called low-income countries. The rich countries, excluding countries of the Middle East and certain other small countries are generally called development countries.
Question 36.1.
Explain the significance of per capita income.
Answer:
Per capita income enables comparisons between countries and provides insights into the relative economic performance and living standards across different nations. It also serves as an important indicator of the standard of living in a country.
Question 36.2
What are the classifications of countries based on per capita income, and which entity is responsible for determining these classifications? [2]
Answer:
The countries are classified into high-income or rich countries and low-income countries based on their per capita income. If the per capita income is US$ 49,300 per annum, it will be classified as a rich country and if the per capita income is US$ 2500 per annum, it will be called a poor country The World Bank determines these classifications.
Section F
Section F consists of Map based questions of 5 marks
Question 37.
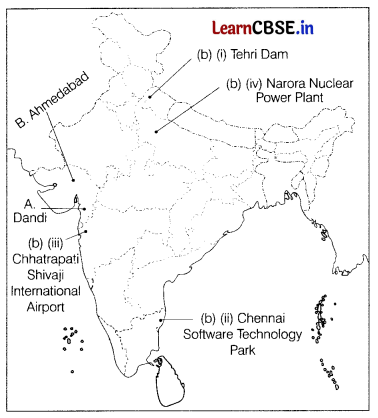
(a) Two places A and B are marked on that given outline map of India. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them. (2)
A. A place where the Civil Disobedience Movement started.
B. A place where Gandhiji went to organize a Satyagraha Movement amongst cotton mill workers.
(b) On the same map of India, locate and label any three among the following with suitable symbols. (3)
(i) Tehri Darn
(ii) Chennai Software Technology Park
(iii) Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport
(iv) Narora Nuclear Power Plant
Answer: