CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Maths 2015 Outside Delhi
Time allowed: 3 hours
Maximum marks : 100
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper consists of 29 questions divided into four sections A, B, C and D. Section A comprises of 4 questions of one mark each, Section B comprises of 8 questions of two marks each, Section C comprises of 11 questions of four marks each and Section D comprises of 6 questions of six marks each.
- All questions in Section A are to be answered in one word, one sentence or as per the exact requirement of the question.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choice has been provided in 1 question of Section A, 3 questions of Section B, 3 questions of Section C and 3 questions of Section D. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all such questions.
- Use of calculators is not permitted. You may ask for logarithmic tables, if required.
**Answer is not given due to the change in present syllabus
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Maths 2015 Outside Delhi Set I
Section – A
Question 1.
Write the value of [1]
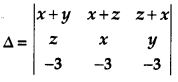
Solution:

Question 2.
Write the sum of the order and degree of the following differential equation: [1]
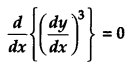
Solution:
Given,
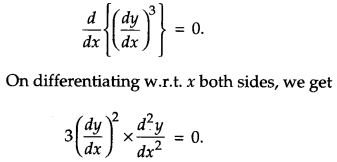
Since the order and degree of the differential equation is 2 and 1 respectively.
So, the sum of the order and degree is 3.
Question 3.
Write the integrating factor of the following [1]
![]()
Solution:
Given,
![]()
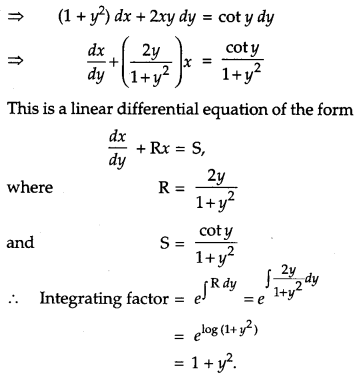
Question 4.
If \(\hat{a}, \hat{b} \text { and } \hat{c}\) are mutually perpendicular unit vectors, then find the value of \(|2 \hat{a}+\hat{b}+\hat{c}|\). [1]
Solution:
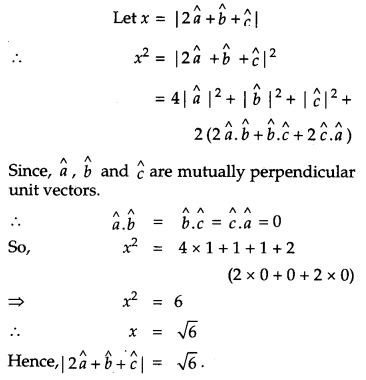
Question 5.
Write a unit vector perpendicular to both the vectors \(\vec{a}=\hat{i}+\hat{j}+\hat{k} \text { and } \vec{b}=\hat{i}+\hat{j}\). [1]
Solution:
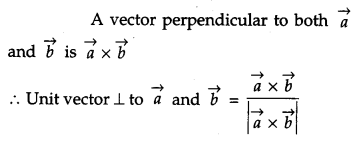
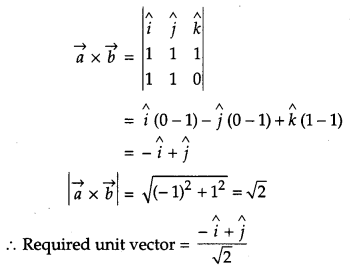
Question 6.
The equations of a line are 5x – 3 = 15y + 7 = 3 – 10z. Write the direction cosines of the line. [1]
Solution:
Given line is 5x – 3 = 15y + 7 = 3 – 10z
Rewritting the eq. in standard form :

Section – B
Question 7.
To promote the making of toilets for women, an organisation tried to generate awareness through
(i) house calls
(ii) letters, and
(iii) announcements. The cost for each mode per attempt is given below:
(i) ₹ 50
(ii) ₹ 20
(ii) ₹ 40
The number of attempts made in three villages X, Y and Z are given below:

Find the total cost incurred by the organisation for the three villages separately, using matrices. Write one value generated by the organisation in the society. [4]
Solution:
The number of attempts made in three villages X, Y and Z can be represented by the 3 × 3 matrix.
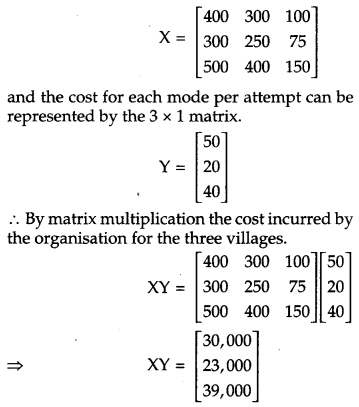
Hence the total cost incurred by the organisation for the three villages separately are ₹ 30,000, ₹ 23,000 and ₹ 39,000.
The organisation in the society generated the value of cleanliness for the women welfare.
Question 8.
Solve for x:
tan-1(x + 1) + tan-1 (x -1) = tan-1\(\frac{8}{31}\) [4]
Solution:
Given, tan-1(x + 1) + tan-1 (x – 1)
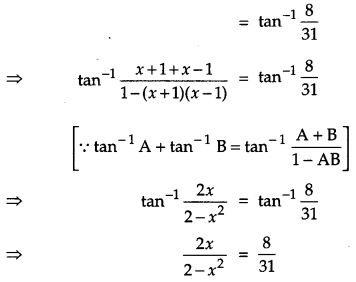

OR
Prove the following:
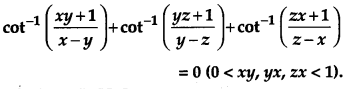
Solution:
L . H. S
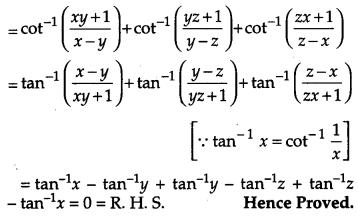
Question 9.
Using properties of determinants, prove the following: [4]
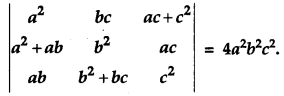
Solution:

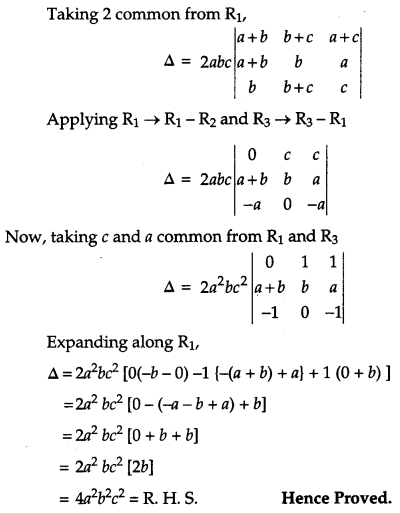
Question 10.
Find the adjoint of the matrix:
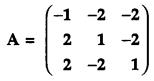
and hence show that A. (adj A) = | A | I3. [4]
Solution:
We have,
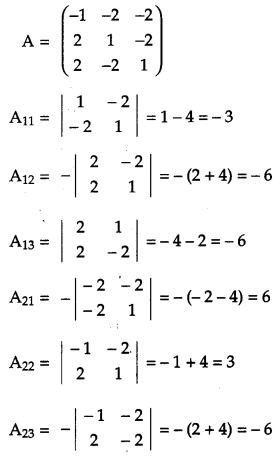
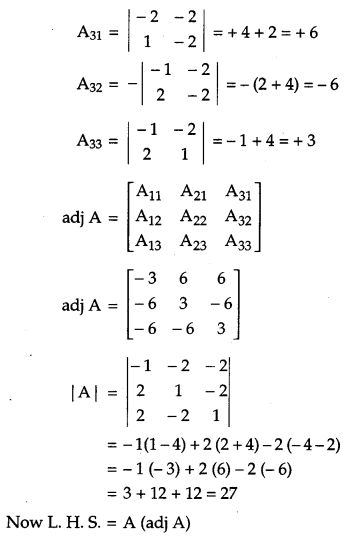
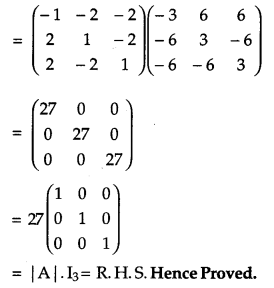
Question 11.
Show that the function f(x) = |x – 1| + |x + 1|, for all x ϵ R, is not differentiable at the points x = -1 and x = 1. [4]
Solution:
Given,
f(x) = | x – 1 | + | x + 1 |
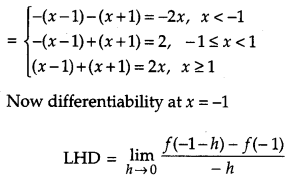
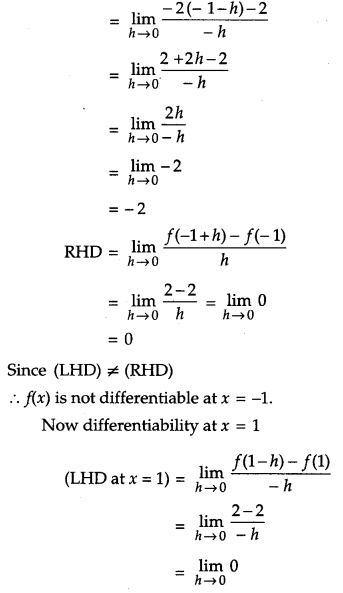
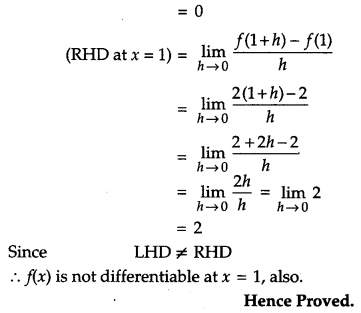
Question 12.
If y = em sin-1x, then show that [4]
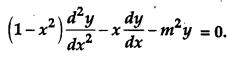
Solution:
Given,
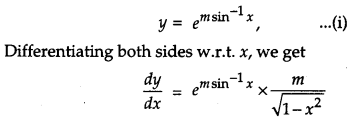
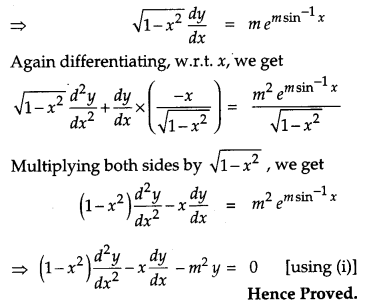
Question 13.
If f(x) = \(\sqrt{x^{2}+1}\); g(x) = \(\frac{x+1}{x^{2}+1}\) and h(x) = 2x – 3, then find f’ [h’ {g'(x)}]. [4]
Solution:
Given,
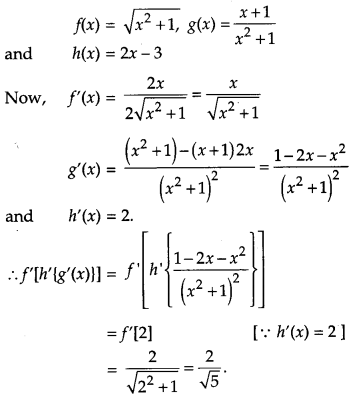
Question 14.
Evaluate: [4]
![]()
Solution:
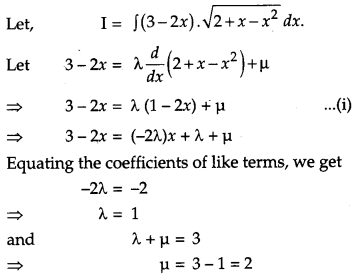
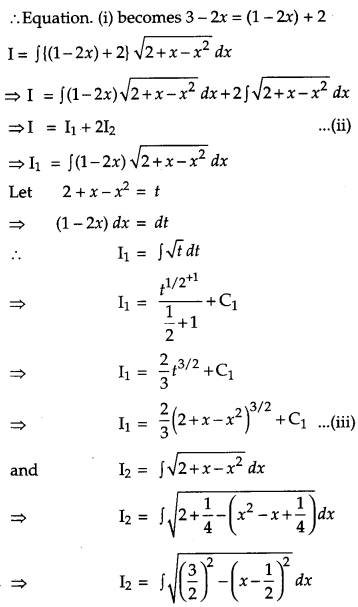
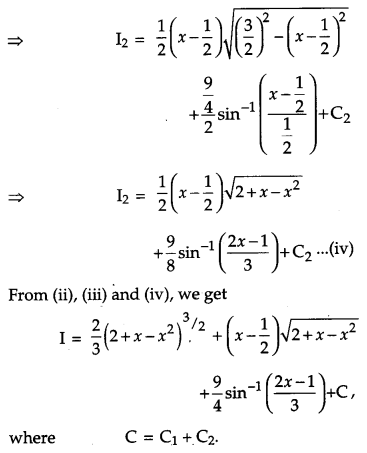
OR
Evaluate:
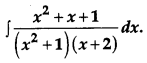
Solution:
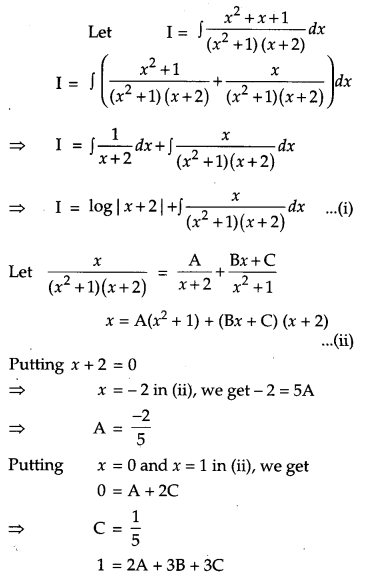
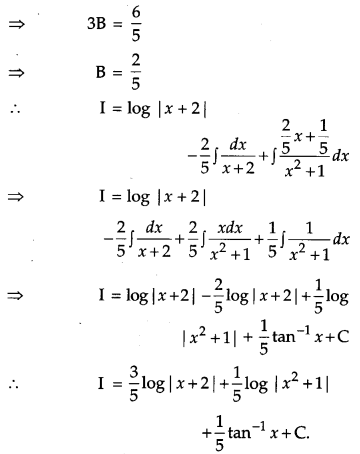
Question 15.
Find [4]
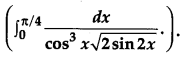
Solution:
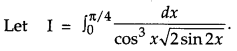
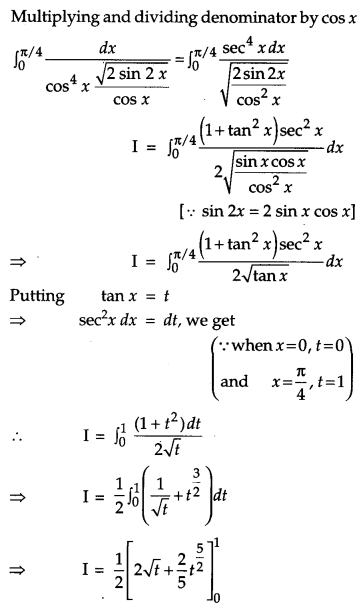
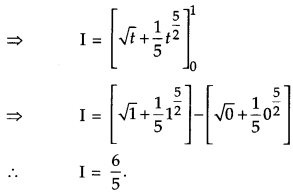
Question 16.
Find [4]
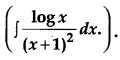
Solution:
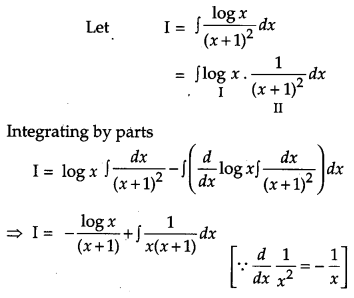
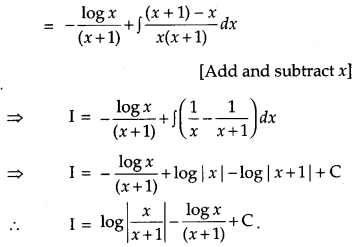
Question 17.
If \(\vec{a}=\hat{i}+2 \hat{j}+\hat{k}, \vec{b}=2 \hat{i}+\hat{j} \text { and } \vec{c}=3 \hat{i}-4 \hat{j}-5 \hat{k}\) then find a unit vector perpendicular to both of the vectors \((\vec{a}-\vec{b}) \text { and }(\vec{c}-\vec{b})\). [4]
Solution:
Here,
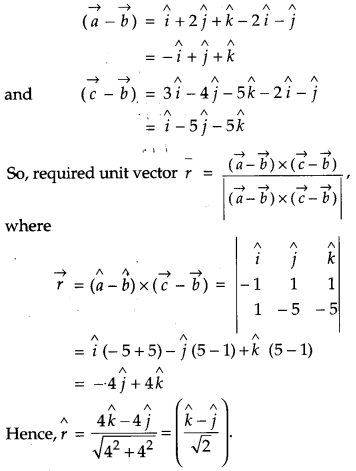
Question 18.
Find the equation of a line passing through the point (1, 2, – 4) and perpendicular to two lines
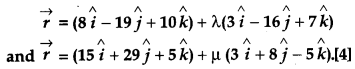
Solution:
Let the direction ratios of required line be a, b, c, since, the line is perpendicular to
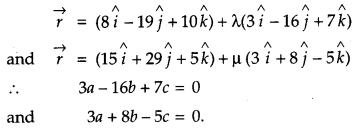

OR
Find the equation of the plane passing through the points (-1, 2, 0), (2, 2, -1) and parallel to the line \(\frac{x-1}{1}=\frac{2 y+1}{2}=\frac{z+1}{-1}\).
Solution:
The equation of a plane passing through (-1, 2, 0) is
a (x + 1) + b (y – 2) + c (z – 0) = 0 …(i)
It passes through (2, 2, -1)
∴ a(2 + 1) + b(2 – 2) + c(-1 – 0) = 0
3a + 0b – c = 0 …(ii)
The given line is

Question 19.
Three cards are drawn successively with replacement from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of spades. Hence find the mean of the distribution. [4]
Solution:
Let X denote the number of spades when three cards are drawn, then, X is a random variable that can take values 0, 1, 2, 3.
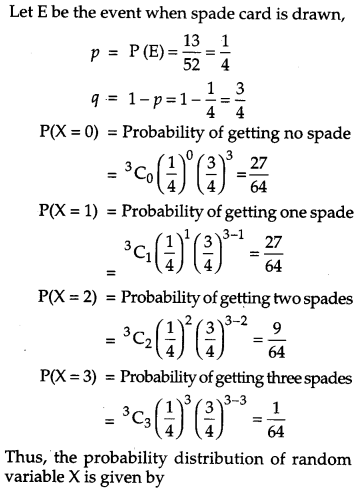
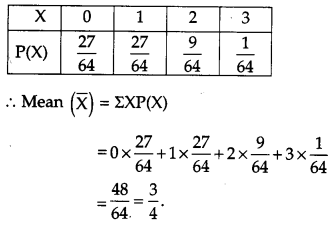
OR
For 6 trials of an experiment, let X be a binomial variate which satisfies the relation 9P(X = 4) = P(X = 2). Find the probability of success.
Solution:
Let p denote the probability of getting success and q be the probability of failure.
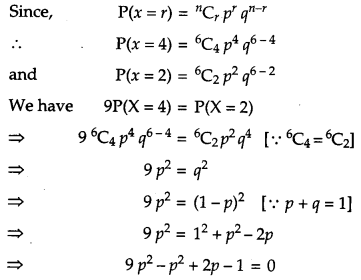
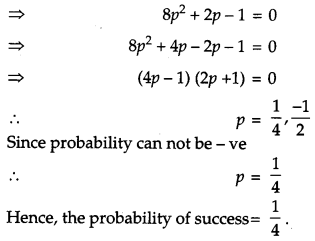
Section – C
Question 20.
Consider f : R+ → [- 9, ∞) given by f(x) = 5x2 + 6x – 9. Prove that f is invertible with [6]
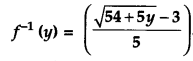
Solution:
To prove f is invertible we have to prove that f is one-one and onto.
For one-one
Let x1, x2 ϵ R+, then
f(x1) = f(x2)
⇒ 5x12 + 6x1 – 9 = 5x22 + 6x2 – 9
⇒ 5(x12 – x22) + 6(x1 – x2) = 0
⇒ (x1 – x2) (5x1 + 5x2 + 6) = 0
⇒ x1 – x2 = 0 as 5x1 + 5x2 + 6 ≠ 0
⇒ x1 = x2
i.e., f is one-one function.
For onto
Let f(x) = y
∴ y = 5x2 + 6x – 9
∴ 5x2 + 6x – (9 + y) = 0
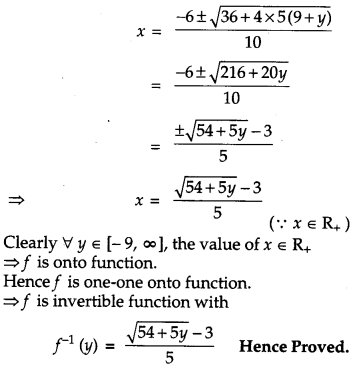
OR
A binary operation * is defined on the set x = R – {-1} by x * y = x + y + xy, ∀ x, y ϵ X. Check whether * is commutative and associative. Find its identity element and also find the inverse of each element of X.**
Question 21.
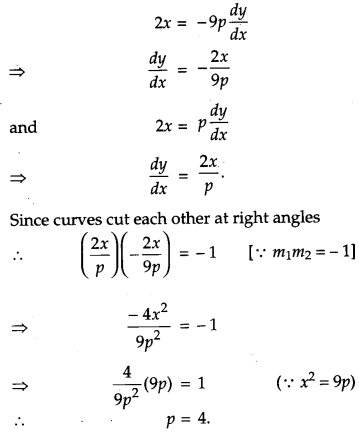
Find the value of p for which the curves x2 = 9p(9 – y) and x2 = p(y + 1) cut each other at right angles. [6]
Solution:
Given,
x2 = 9p(9 – y) …(i)
and x2 = p (y +1) …(ii)
From (i) and (ii), we get
9p (9 – y) = p(y + 1)
⇒ 81p – 9py = py + p
⇒ 10py =80 p
⇒ y = 8
x2 = 9p
Now, differentiating (i) and (ii) w.r.t. x, we get
Question 22.
Using integration, prove that the curves y2 = Ax and x2 = 4y divide the area of the square bounded by x = 0, x = 4, y = 0 and y = 4 into three equal parts. [6]
Solution:
Given,
y2 = Ax …(i)
and x2 = 4y ……(ii)
Solving (i) and (ii), we get the point of intersection (0, 0) and (4, 4).
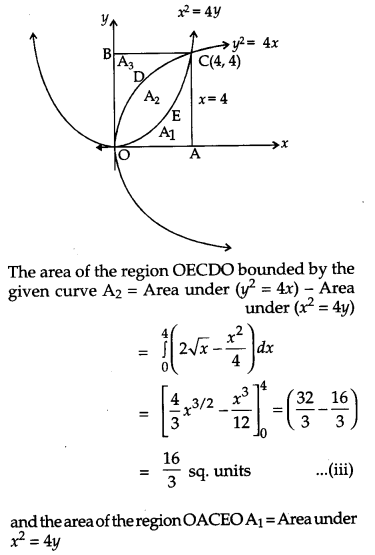
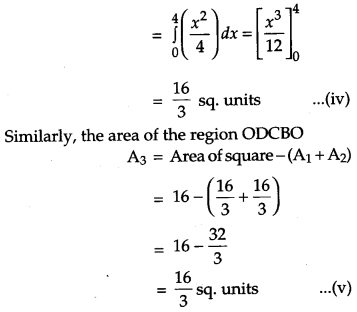
From (iii), (iv) and (v), it can be concluded that the given curves divide the area of the square bounded by x = 0, x = 4, y = 0 into three equal parts. Hence Proved.
Question 23.
Show that the differential equation \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{y^{2}}{x y-x^{2}}\) is homogeneous and also solve it. [6]
Solution:
We have

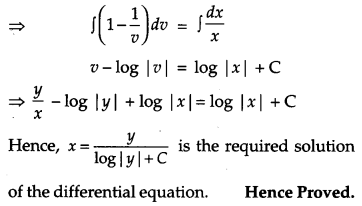
OR
Find the particular solution of the differential equation (tan-1y – x) dy = (1 + y2) dx, given that x = 1, when y = 0.
Solution:
Given,
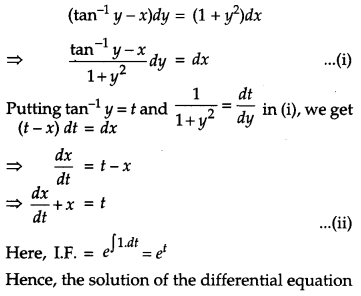

Question 24.
Find the distance of the point P(3, 4, 4) from the point, where the line joining the points A(3, -4, -5) and B(2, -3, 1) intersects the plane 2x + y + z = 7. [6]
Solution:
Equation of the line joining the points A(3, -4, -5) and B(2, – 3, 1) is

Question 25.
A company manufactures three kinds of calculators : A, B and C in its two factories I and II. The company has got an order for manufacturing at least 6400 calculators of kind A, 4000 of kind B and 4800 of kind C. The daily output of factory I is of 50 calculators of kind A, 50 calculators of kind B, and 30 calculators of kind C. The daily output of factory II is of 40 calculators of kind A, 20 of kind B and 40 of kind C. The cost perdaytorunfactorylis ₹ 12,000 and of factory II is ₹ 15,000. How many days do the two factories have to be in operation to produce the order with the minimum cost ? Formulate this problem as an LPP and solve it graphically. [6]
Solution:
Let the factories I and II work for x and y number of days respectively.
Thus, the given linear programming problem is Minimize Z = ₹ (12000x + 15000y)
Subject to the constraints
50x + 40y ≥ 6400
50x + 20y ≥ 4000
30x + 40y ≥ 4800
x ≥ 0
and y ≥ 0 .
i.e. 5x + 4y ≥ 640
5x + 2y ≥ 400
3x + 4y ≥ 480
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
To solve this L. P. P,
Let us consider the equations
L1 : 5x + 4y = 640 …(i)
L2 : 5x + 2y = 400 …(ii)
L3 : 3x + 4y = 480 …(iii)
The point of intersection of L1 and L2 is D(32, 120) and that of L1 and L3 is C (80,60)
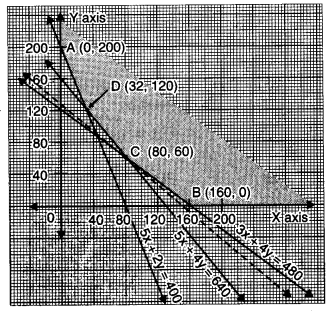
The shaded region is the solution region of the given L. P. P.
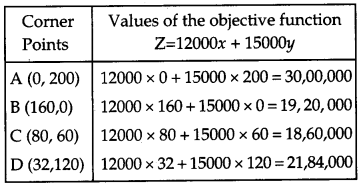
Out of these values of Z, the minimum value of Z is 18,60,000 at x = 80 and y = 60.
Since the feasible region is unbounded so we draw the graph of inequality
12000 x + 15000 y < 1860000
i. e., 4x + 5y ≤ 620
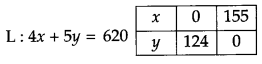
We observe that open half one represented by L have no point common with feasible region.
Z = 12000 × 80 + 15000 × 60
= ₹ 18,60,000.
Hence, the factories I and II work for 80 and 60 number of days respectively.
Question 26.
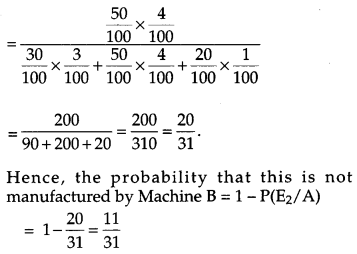
In a factory which manufactures bolts, machines A, B and C manufacture respectively 30%, 50% and 20% of the bolts. Of their outputs 3, 4 and 1 percent respectively are defective bolts. A bolt is drawn at random from the product and is found to be defective. Find the probability that this is not manufactured by machine B. [6]
Solution:
Let E1, E2, E3 and A be the events defined as below
E1 = the bolt is manufactured by machine A.
E2 = the bolt is manufactured by machine B.
E3 = the bolt is manufactured by machine C.
A = the bolt is defective.
then, P(E1) = Probability that the bolt drawn is manufactured by machine A = \(\frac{30}{100}\)
P(E2) = Probability that the bolt drawn is manufactured by machine B = \(\frac{50}{100}\)
P(E3) = Probability that the bolt drawn is manufactured by machine C = \(\frac{20}{100}\)
P(A/E1) = Probability that the bolt drawn is defective given that it is manufactured by machine A.

All questions are same in Outside Delhi Set II and Set III