Class 12 History Notes Chapter 1 Bricks, Beads and Bones The Harappan Civilisation
- Harappan Civilisation is also known as Indus Valley Civilisation. It is the oldest Civilisation of India.
- There is no consensus about the chronology of the Harappan Civilisation.
- Various scholars have given different dates about this period.
- According to Sir John Marshall, “this civilisation flourished between 3250 and 2750 BCE”.
- It was Daya Ram Sahni, who first discovered the sites of Harappan in 1921.
- The main centres of this civilisation are in Pakistan. The same famous sites of this civilisation (now in Pakistan) are Mohenjodaro and Chanhudaro.
- The main centre where this Civilisation flourished in India are Kalibangan, Sangol, Pengplor, Lothal, Dholavira and Banawali.
- The urban planning of this civilisation was very magnificent. The houses were built in a systematic manner. Roads were wide and cut each other at right angle.
- The people of Indus Valley Civilisation had also made best planning for the drainage of rainwater and dirty water.
- The caste system was not present in the society. All the people lived together with mutual love and understanding.% The women held a high position or rank in the society.
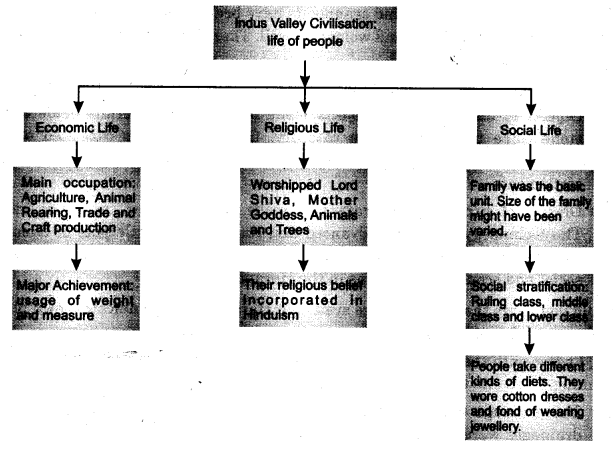
- They were fond of fashion. The economic life the people was very prosperous.
- The main occupations of the people were the agriculture and domestication of animals.
- Trade was well developed. Both maternal and external trade was carried out.
- The people worshipped many gods and goddesses. They worshipped mother goddesses, Lord Shiva, animal, birds, trees and the Sun.
- They knew arts and crafts. They knew the art of making beautiful sculptures, toys, pottery, ornaments, etc. They were skilled in the production of seals.
- The languages used by them on the seals is still to be deciphered. If one is able to decipher their script inscribed on the seals, it will throw a flood of the light on the various aspects of the Harappan Civilisation.
- The main sources of our information of Harappan Civilisation is archaeological materials. The excavation carried out at Indus sites tries to reconstruct the history of this civilisation.
- During the excavation of Indus sites, many tools, pottery, seals, household objects, etc. have excavated.
- All these excavated materials are deeply examined by the archaeologists.
- Many historians like Cunningham, R.E.M. Wheeler, John Marshall and G.F.
- Dates have played a valuable role in reconstructing the history of the ancient past including the Indus Valley Civilisation sites.
- Many Indian archaeologists like Daya Ram Sahni, S.R. Rao, R.S. Bisht and B.K. Thapar have played a great role in excavations of the Indus sites.
- Indus Valley Civilisation is also known as Bronze Age Civilisation, because people used bronze extensively for making their pottery, figure lines and ornaments.
- Almost 1900 BCE, these were explicit signs about the decline of this civilisation.
- By this time the two most important cities of Indus Valley-Mohenjodaro and Harappa had been completely declined.
- Around 1200 BCE, this civilisation had completely vanished. Epidemic, Aryan Invasion, change in the course of the river Indus, excessive floods, earthquake, etc. may be the main reasons for the decline of this civilisation.
rcheological Evidences of The Harappan Civilisation:
- The Harappan Civilisation is also known as Indus Valley Civilisation. This civilisation is dated between BCE 2600 and 1990 BCE. It is the oldest civilisation of India. We know about the civilisation from archaeological evidences like houses, pots, ornaments, tools and seals used by the people of that period.
- There were also earlier and later cultures, known as Early Harappan and Late Harappan Civilisation.
- Cunningham was the first Director General of Archaeological Survey of India who began archaeological excavations in the Harappan sites.
- Cunningham was unable to find the significance of Harappan Civilisation and thought that Indian history began with the first cities in the Ganga valley.
- Daya Ram Sahni, Rakhal Das Baneiji, John Marshall were some of the important archaeologists associated with the discovery of Harappan Civilisation. The frontiers of the Harappan civilisation have no connection with present day national boundaries. The major sites are now in Pakistani territory.
- In India, a number of Harappan settlements were found in Punjab and Haryana. The main centres where this civilisation flourished in India are Kalibangan, Lothal, Dholavira, Rakhi Garhi and Banawali.
- Archaeologist tried to classify artefacts in terms of material and in terms of function by comparing these with present-day things. The problems of archaeological interpretation are most evident in attempts to reconstruct religious practices of the Harappan.
- Unusual objects like terracotta figurines of women, stone statuary of men, motif of unicorn and figure in yogic posture on seals and structures like the great bath and fire altars may have had a religious significance. Several reconstructions regarding the Harappan civilisation remain speculative at present and there is a vast scope for future work.
Seals, Script, Weights of Harappan Civilisation:
- Seals and sealings were used to facilitate long distance communication. If the bag of goods reached with its sealing intact, it meant that it had not been tampered with. Seals also conveyed the identity of the sender.
- The Harappan script remains undeciphered to date. The script was not alphabetical and had many signs between 375 and 400.
- Exchange were regulated by a precise system of weights, usually made of a stone called chert with no marking. The lower denominations of weights were binary7 and the higher denominations followed the decimal system.
Food Habits of Harappan People:
- The people of Harappan Civilisation ate a wide range of plant and animal products including fish and meat, wheat, maize, millet, pulses, rice and another eatables. For this, cattle, sheep, goat, buffalo and pig were domesticated by the Harappans.
Agricultural Techniques Using by Harappan People:
- Archaeological evidences suggested that oxen were used for ploughing and two different crops were grown together. As most of the Harappan sites are located in Semi-arid lands, it is evident that water from canals and wells was used for irrigation.
Social and Economic Differences among Harappan People:
- Archaeologists use certain strategies to find out social and economic differences among people. These include studying burials and artefacts which can be divided into utilitarian and luxuries.
- Valuable materials are generally concentrated in large settlements, but rarely found in smaller settlements.
Craft Production of Harappan People:
- Harappans knew the art of making beautiful sculptures, toys, pottery, ornaments, etc. Chanhudaro was a tiny settlement exclusively devoted to craft production, including bead-making, shell-cutting, metal-working, seal-making and weight-making.
- Grinding, polishing and drilling were done for making beads. Nageshwar and Balakot were specialised centres for making shell objects as both these settlements are near the coast. Apart from smaller settlements, larger cities like Mohenjodaro and Harappa were also the specialised centres for craft production.
Acquiring Materials for Craft:
- The Harappans procured materials for craft production in various ways. Sometimes they established settlements where raw materials were available. Another strategy for procuring raw materials may have been to send expeditions to areas where these were available e.g. Khetri region for copper (Rajasthan) and South India for gold.
- The Harappan made contact with distant lands like Oman for procuring copper. The Harappan seals, weights, dice and beads were found in other countries, Oman, Bahrain and Mesopotamia.
Economic Life and Trade during Harappan Civilisation:
- Economic life of the people was very prosperous The main occupations of the people were agriculture and domestication of animals.
- Trade was well developed. Both internal and external trade were carried out. Pictures of ships, boats have also been found on seals which throw light on Harappan contacts with far off places
Religious Belief of Harappan People:
- People of this civilisation worshipped many Gods and Goddesses. They worshipped Lord Shiva, mother Goddesses, animals, birds, trees and the sun.
Caste System in Harappan Civilisation:
- The caste system was not present in the society. All people live together with mutual love and understanding. Women held a high position or rank in the society.
A Planned Town of Harappan Civilisation Mohenjodaro:
- Mohenjodaro was the most well-known urban site of the Harappan Civilisation. Although Harappa was the first site to be discovered, it was badly destroyed by brick robbers.
- The settlement in Harappan civilisation was divided into two sections, one smaller in terms of land but higher in terms of power known as the Citadel, the other much larger in terms of area but lower in terms of power was known as Lower Town.
- All the Harappan cities had carefully planned drainage system. The residential buildings at Mohenjodaro were centred on a courtyard, had its own bathrooms, the drains of which were connected to the street drains.
- In Mohenjodaro, many houses had well and their estimated number was about 700. Structures like warehouse and the Great Bath’ were used for public purposes.
The End of Harappan Civilisation:
- By 1800 BCE, most of the mature Harappan sites were abandoned. Around 1200 BCE, this civilisation had completely vanished. After 1900 BCE, a rural way of life what was known as ‘Late Harappan’ or ‘successor cultures’ emerged.
- The reasons for the end of the civilisation range from climatic change, deforestation, excessive floods, the shifting and drying up of rivers and to overuse of the landscape. All these factors may have weakened the civilisation, but its ultimate extinction is more likely to have been completed by deliberate and large-scale destruction or by an invasion.
Class 12 History Notes Chapter 1 Important Terms:
- Seal: It generally contained animal motifs and signs from a script.
- Hoards: Generally metal objects and jewellery kept by people inside containers.
- Stratigraphy: The study of historical layers.
- Motif: Name of animal, used by the Harappans on seals to mark some sort of trademark.
- Proto-Shiva: A seal that shows a figure seated in a yogic posture surrounded by animals has been designated as Proto-Shiva, an early form of one of the deities of Hinduism.
- Lingas: The polished stones were often worshipped as symbols of the God Shiva.
- Shamans: These were the groups of men and women who claimed to have magical and healing powers and ability to communicate with the other world.
- Art: It referred to painting, sculpture, pottery and seal making.
- Culture: Term used for a group of objects, distinct in style, found specifically within a geographical area and period of time.
- Pictographs: Picture-like signs to represent letters or words.
- The Great Bath: Best known building in Mohenjodaro for bath.
- Granaries: Buildings where grains were stored.
Time Line:
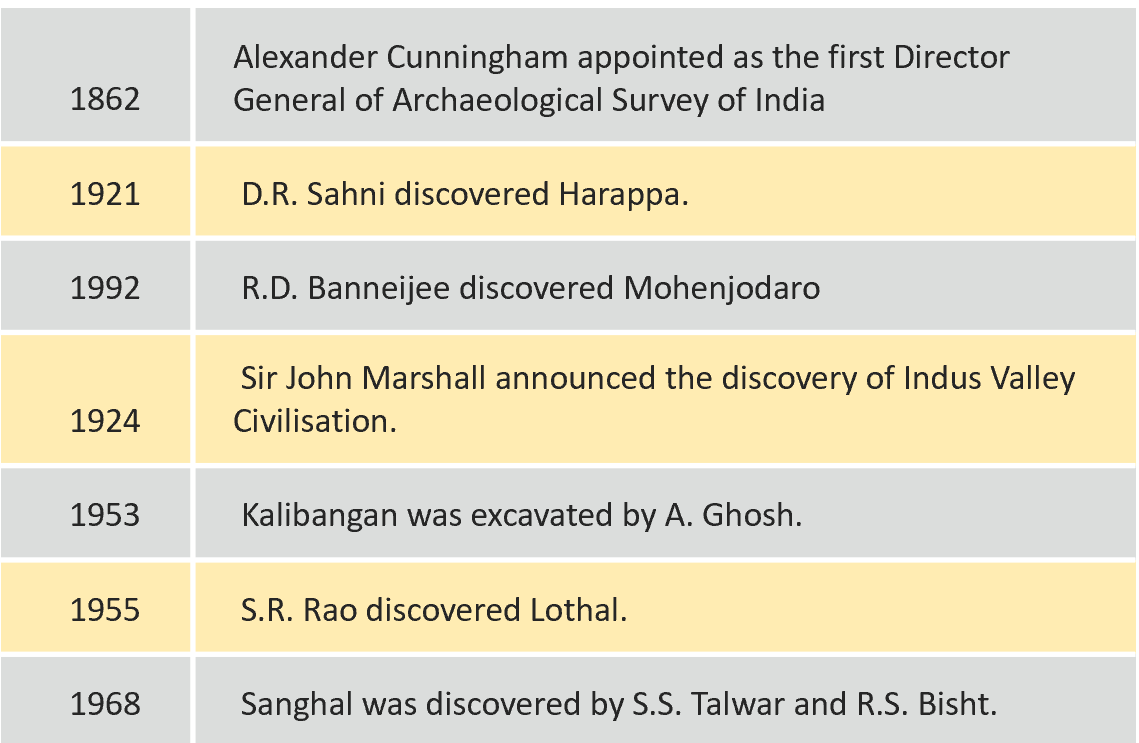
- 1862 Alexander Cunningham appointed as the first Director General of Archaeological Survey of India.
- 1921 D.R. Sahni discovered Harappa.
- 1992 R.D. Banneijee discovered Mohenjodaro
- 1924 Sir John Marshall announced the discovery of Indus Valley Civilisation.
- 1953 Kalibangan was excavated by A. Ghosh.
- 1955 S.R. Rao discovered Lothal.
- 1968 Sanghal was discovered by S.S. Talwar and R.S. Bisht.